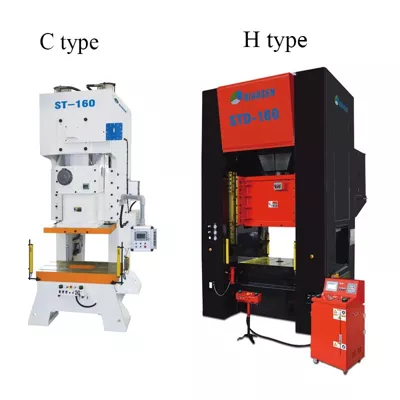
Pneumatic punch press VS Hydraulic punch press

Pneumatic Punch Press VS Hydraulic Punch Press
In the field of metalworking, two commonly used machines for punching holes and shaping metal sheets are the pneumatic punch press and the hydraulic punch press. Although both machines serve similar purposes, they differ in their underlying mechanisms, performance, and applications. This article aims to explore the main differences between pneumatic punch presses and hydraulic punch presses, covering their working principles, advantages, disadvantages, and suitable applications.
Working Principles
The basic working principle of a pneumatic punch press involves converting air pressure into mechanical force. It utilizes compressed air to control the movement of a ram that performs the punching or shaping operation. When the air pressure is released, the ram retreats to its original position. On the other hand, a hydraulic punch press relies on fluid pressure to generate mechanical force. It utilizes a hydraulic system, including a pump, hydraulic fluid, and cylinders, to control the movement of the ram. By regulating the flow of hydraulic fluid, the ram can move up and down to carry out the punching or shaping operation.
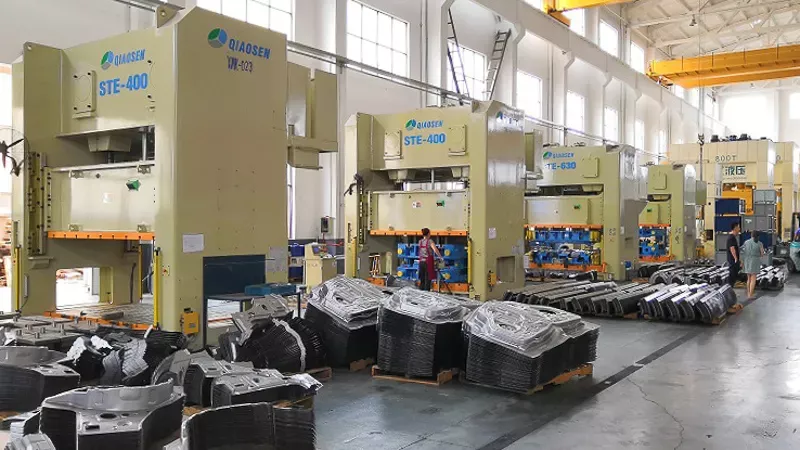

Performance Comparison
Pneumatic punch presses and hydraulic punch presses exhibit noticeable performance differences. Pneumatic punch presses generally offer faster cycle times due to their ability to quickly retract the ram. This makes them suitable for high-speed punching or forming operations. However, their maximum force output is limited compared to hydraulic punch presses. Hydraulic punch presses, on the other hand, can exert much higher force thanks to their hydraulic systems. This enables them to handle heavier gauge materials and perform deep hole punching. Although hydraulic punch presses may have slightly longer cycle times due to the slower retraction of the ram, their versatility in terms of force output makes them ideal for a wide range of applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Pneumatic punch presses and hydraulic punch presses each have their unique advantages and disadvantages. Pneumatic punch presses are generally more affordable and require less maintenance compared to hydraulic punch presses. They also produce less noise and vibration, making them more suitable for environments with noise restrictions. However, pneumatic punch presses have limitations in terms of the force they can generate and the thickness of the materials they can handle. Hydraulic punch presses, on the other hand, offer higher force capabilities, allowing them to process thicker and tougher materials. They also provide more versatility in terms of adjustability and control. However, hydraulic punch presses tend to be more expensive, require regular maintenance of the hydraulic system, and generate more noise and vibration.
Applications
The choice between a pneumatic punch press and a hydraulic punch press largely depends on the specific application requirements. Pneumatic punch presses are often chosen for light-duty applications that involve thin materials, such as electronics manufacturing and small-scale metalworking. Their fast cycle times and affordable cost make them ideal for high-volume production. On the other hand, hydraulic punch presses excel in heavy-duty applications that involve thicker materials, such as automotive manufacturing and construction. Their high force output allows them to handle challenging tasks like deep hole punching, bending, and flanging. The adjustability and control provided by the hydraulic system make them suitable for precision operations.
In summary, pneumatic punch presses and hydraulic punch presses differ in their working principles, performance, advantages, disadvantages, and suitable applications. Pneumatic punch presses are characterized by their reliance on compressed air, faster cycle times, and affordability. They are suitable for light-duty applications but have limitations in force output and material thickness. Hydraulic punch presses utilize hydraulic fluid for generating high force, making them suitable for heavy-duty operations. They offer greater versatility but come at a higher cost and require more maintenance. By understanding their differences, manufacturers can choose the most appropriate punch press for their specific needs.
8years foriegn trade experience Easily grasp customer needs Keeping good relationship with customers









